- What we do
- Services
- Solutions
- Our Works
- Company
- Contact Us
July 15, 2022
Benefits of QA Automation: How It Can Help Your Product
Answers to all embarrassing questions about automated testing that you always wanted to ask but were afraid to. Help yourself!
Testing is an essential part of any development process. It ensures that the software product you launch on the market has the highest possible quality. Users will recognize immediately if the app or a website wasn’t tested before the release. A lot of companies use manual testing to cover all aspects of the app, but automated testing is an efficient option to consider.
The fact that automated testing is expensive often prevents product teams from turning to it at the very beginning of the project. In this article, we answer the most common questions our clients usually ask us about automated testing, when it's the best time on the project timeline to embark on test automation, and try to figure out how it can help teams be more efficient.
What is automated testing?
Well, it’s clear from the name itself that there is no “handicraft” in automated testing. Basically, everything that is done by humans in manual testing, is performed by software tools and scripts in automated testing. For example, in automated UI tests, the script fully imitates the way an ordinary user interacts with the application to check whether the interface responds to user actions as it should.
However, humans still play a big part in automation testing when it comes to developing testing frameworks and scripts, as well as keeping them up-to-date. This is done by automated test engineers—first-class specialists, who are well-versed both in engineering and QA testing. As for tools and scripts, they are used mostly for repetitive tasks that can easily be programmed, such as detecting bugs, reporting them in a bug-tracking system, and notifying responsible engineers.
Automated testing vs Manual testing
Automated and manual tests are easy to distinguish even by their names. Automated tests use prewritten scripts to check the code, and manual testing implies an engineer that executes cases on their own. While manual QA engineers need documentation and a correctly prepared dataset on hand to provide full test coverage, automated tests require more preparation.
First, we should define clearly what app functionality will be covered by the tests, ideally with a prototype on hand. Then, we should choose a preferred tool and develop a testing framework to start working. Lastly, it's important to constantly keep an eye on the scripts so that they stay up-to-date as the product functionality changes and gets updated. As you see, it’s a pretty laborious process.
Automated tests are not a magic bullet. They are just scripts that are programmed to check specific things in a certain way, but, unlike humans, they lack improvisation. For example, if a script for browser testing is programmed to check if there are only “two” buttons in a website’s registration form, it won’t report a bug If suddenly a “third” button appears, simply because it's not programmed to do this.
In general, it’s fine if 90% of your product’s repetitive tasks, such as regression and load testing, are performed by automated tests, while the remaining 10% (that cannot be automated and that require human observation), are handled by manual QA engineers.
| Manual | Automated | |
|---|---|---|
| Time | Time-consuming | Fast |
| Accuracy | The risk of human error is higher | More accurate but operates only in set conditions |
| Investments | The initial investments are low, but in the long run, ROI is also low | The initial investments are can be high, but ROI will also be high |
Types of automated testing
It includes a wide range of tests that can be performed on your product. It’s not necessary to use all of them at once, but it’s better to know what they can do when your team tells you what QA your project needs. Here are several types of tests that are considered automated:
- Unit testing: This type is responsible for test coverage for small separate components. It ensures that each part of the code works the right way.
- Smoke testing: It determines whether the current build is stable and ready for further QA testing.
- Integration testing: When all the units are tested separately, the integration tests will check how these components work as a whole.
- Security testing: The name speaks for itself. Security tests look for any vulnerability an app can have.
- Performance testing: It helps you see how your software runs at the highest level of load and how responsive your software is.
- Regression testing: These tests are meant to check if the previously written code functions as it should after being changed.
There are more automated tests that your specialists can perform, but the above-mentioned options are the most common and trustworthy.
How to automate your quality assurance?
To automate your testing process, you need to complete several important steps. They usually happen simultaneously with the development process; the product stays checked at all stages.

1. Define the range of automation
The first step consists of deciding what tests to automate. The most important questions to answer here are:
- What tests can we automate?
- What tests should be automated?
- What level of manual involvement will there be?
- What resources do you need to make it happen?
You also need to take into account some additional factors like level of expertise and available budget.
2. Choosing a toolset
Once you know what to automate, you need to choose a how. There are plenty of automation tools for your team to consider that we will talk about later. Here, you should consider their functionality, flexibility, and price. Also, your team should have clear instructions on how to work with it.
3. Build a strategy
Planning is important in quality assurance. So now your testing team should plan the sets and choose a framework. It should have suitable testing tools and standards, as well as common practices.
4. Create an environment
Next step is building a testing environment. In a nutshell, it’s a server where your testers can run test cases. Besides the server itself, you also should take care of network configuration and appropriate hardware.
5. Write and execute scripts
Here comes the main part: Human testers actually write and implement scripts in a pre-built environment. Test scripts are based on real requirements your product has. Also, your team can reuse them as much as they need.
6. Analyze the results
When the software testing is done, the tool you’ve chosen will create a report with all the bugs that need to be fixed. Your team’s task is to look through it and send the results to developers so they can fix it.
Let's list the QA automation benefits
QA automation is a productive practice to upgrade your app and optimize your team’s workflow. The most prominent benefits of automation testing are
Resource-efficiency
The main advantage of test automation is that it can release manual QA engineers from tiresome and time-consuming work, such as regression testing. Unlike humans, scripts can’t get tired and lose focus from monotonous and repetitive tasks, that’s why they can be much more productive and time-saving than manual tests.
Effort optimization
Moreover, unlike manual tests that require time and effort from a responsible human, automated tests can be performed at any time by any team member. For example, an engineer can run an automated unit test to check a new piece of code immediately after committing it and see the result immediately without having to wait until a QA engineer has time to do the job.
Facilitating calculations
Another advantage of test automation over humans is that automated tests can easily make complex calculations. Let’s say we need to make sure that an algorithm inside a financial application calculates monthly loan payments properly, taking into account various dynamic data, such as interest rate, exchange rate, etc. Apparently, it will take an eternity for a manual QA engineer to check all calculations, while an automated test will handle them instantly.
Fast speed
It's obvious that automated tests can simply work faster than any human, therefore, an iteration of automated testing is much cheaper than manual testing. As a bonus, after the test cycles are over, anyone in the project team can access the report and see all the reported bugs. Moreover, the process of detecting and fixing bugs can be automated even a bit further; for example, upon detecting a bug, the script creates a ticket in a bug-tracking system and then subsequently sends a notification to a responsible engineer.
..and if you want a free consultation from one, just contact us
Get in touchAre there any disadvantages of QA automation?
Despite all the obvious benefits of automation testing, it has its limits. You should consider them before applying such tests to your project.Potentially high initial costs
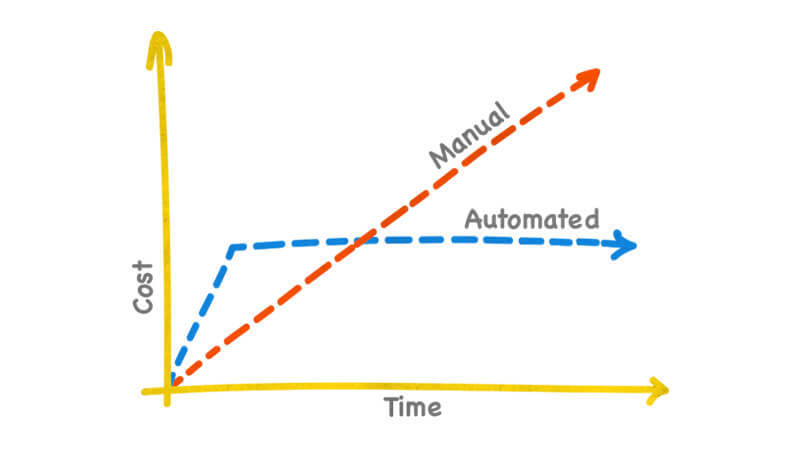
In the beginning, acquiring the necessary tools and hiring experienced specialists for automated testing can cost quite a while. However, it can be less expensive in a long-term project because as the project grows, you’ll have to hire more “manual” QA engineers to test new features and updates, therefore, the cost of manual testing will increase significantly. At the same time, the cost of test automation will remain relatively low and stable because you won’t have to hire more specialists to keep scripts up-to-date.
Time-consuming start
Automation testing does not come out of the blue. Your QA engineers will need time to write the scripts for tests and cover the code with them. If now you don’t have the necessary resources to wait for implementing automated tests, it’s better to start with the manual ones.
Not all tests can and need to be automated
Even though automation is a powerful way to optimize software testing, not every test requires it. Sometimes a human factor can become a huge benefit. For example, usability and UI tests require subjective validation and the script will never be able to determine if the application is comfortable to use. There are also certain restraints for automated UI tests, such as captchas, emails, etc.
Popular tools for automation testing
There are several common solutions QA teams use to provide automated test coverage. These tools are proven to be efficient, easy to use, and convenient. The list includes:

- Selenium. It’s an effective open-source framework for browser testing of web applications. It supports all browsers and platforms and works with most main programming languages.
- Katalan Studio. This tool is one of the most recent ones. It’s suitable for web, mobile, and desktop applications and requires minimal programming skills.
- UTF One. Previously known as UTF, this tool is available for testing all types of software we already mentioned plus it can test RPA applications.
- IBM Rational Functional Tester. IBM RFT is able to test apps written in different languages and tools like .Net, Java, SAP, Visual Basic, and Adobe Flex.
The list can include more tools that will be most suitable for your tasks, but it represents the most common and trusted solutions for automation testing.
Conclusion
If you are still not sure where to start test automation, the general recommendation is the following: if you know exactly what your product should be in the future and you don’t plan any major changes and revamps, be sure to embark on test automation as soon as possible.
Again, don’t think that automated testing will solve all your problems, though, a well-blended mix of manual and automated tests has the possibility of doing this. Automated tests lack intellect, at least for the time being, but when the human intellect joins the speed and accuracy of machines, they make a dynamic duo. Don’t hesitate to benefit from it (and drop us a line:)
Read also:
✓ Benefits of Load Testing and Its Disadvantages
✓ Software Testing Options That Will Improve Your Product
Got a project in mind?
Fill in this form or send us an e-mail
🤖 What is automated testing?
🤖 What are the benefits of automation testing?
🤖 Are there any drawbacks of automated testing?
🤖 What automated tests can my team use?
Subscribe to new posts.
Get weekly updates on the newest design stories, case studies and tips right in your mailbox.
